Caffeine, a stimulant found in coffee, tea, and various other beverages, has been a part of human culture for thousands of years. Revered for its ability to ward off sleepiness and enhance focus, caffeine is the most widely consumed psychoactive substance globally. However, like any potent compound, it’s a double-edged sword. This article delves into the multifaceted world of caffeine, exploring its health benefits and the complications arising from overconsumption.

Understanding Caffeine: Caffeine is a natural stimulant that primarily affects the central nervous system, where it reduces fatigue and drowsiness. Typically, it’s found in coffee beans, tea leaves, and cacao pods. It’s also added to certain soft drinks and energy drinks, as well as some medications.
The Health Benefits of Caffeine:
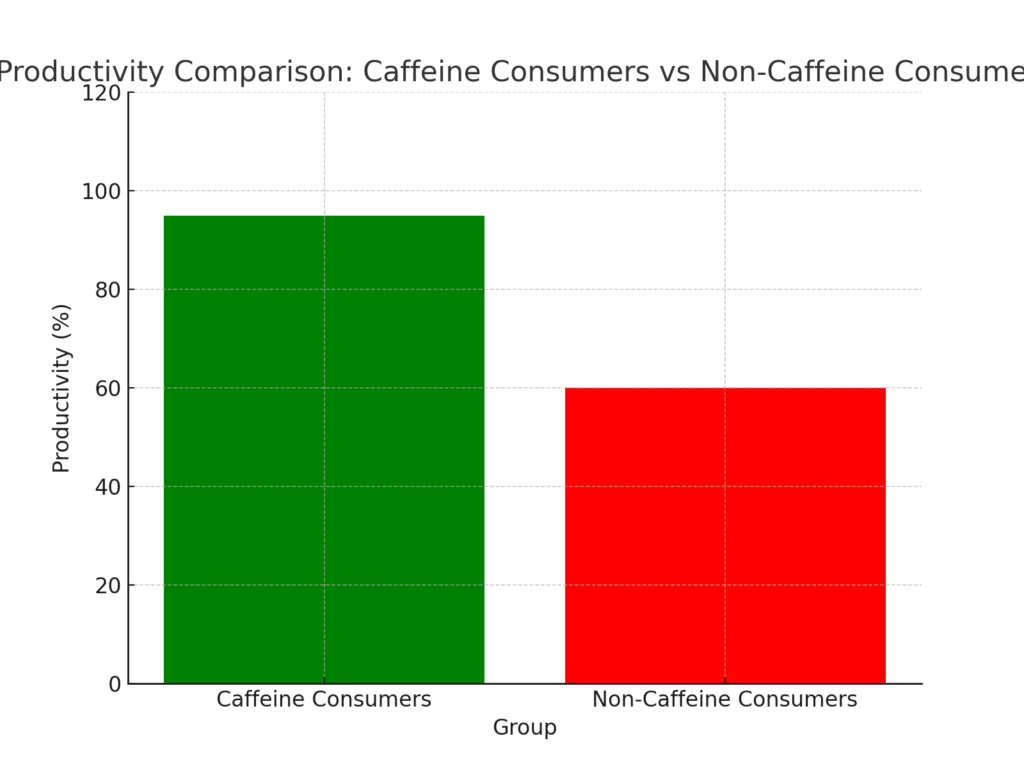
- Improved Mental Alertness: Caffeine’s most notable benefit is its ability to enhance mental alertness and cognitive function. It blocks adenosine, a neurotransmitter that relaxes the brain and makes you feel tired.
- Increased Metabolism and Weight Loss: Caffeine can temporarily boost metabolism and fat burning. Studies have shown that it can increase your metabolic rate by 3–11%.
- Enhanced Physical Performance: By stimulating the nervous system, caffeine helps to break down body fat, making free fatty acids available as fuel. This process can enhance physical performance by roughly 12%.
- Reduced Risk of Neurological Diseases: Research suggests that caffeine consumption may lower the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
- Heart Health and Diabetes: Moderate caffeine consumption is associated with a lower risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes, although the reasons are not entirely clear.

The Downside of Caffeine: While caffeine offers numerous health benefits, excessive intake can lead to several complications. These include:
- Anxiety and Restlessness: High doses of caffeine can lead to increased anxiety, restlessness, and even panic attacks in sensitive individuals.
- Sleep Disturbances: Caffeine can interfere with sleep patterns, reducing the quality and duration of sleep, especially if consumed later in the day.
- Digestive Issues: Large amounts of caffeine can lead to digestive discomfort and exacerbate conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
- Addiction and Withdrawal Symptoms: Regular, high consumption of caffeine can lead to physical dependence, and withdrawal can cause symptoms like headaches, fatigue, and irritability.
- Cardiovascular Problems: Though moderate caffeine intake is generally safe for the heart, excessive consumption can increase heart rate and blood pressure.

How Much is Too Much? The recommended caffeine limit for most healthy adults is up to 400 milligrams (mg) per day – roughly the amount in four 8-ounce cups of brewed coffee. However, individual tolerance varies. Factors like age, body weight, and overall health can influence how much caffeine someone can consume without adverse effects.
Conclusion: Caffeine, when consumed in moderation, can be a healthy part of your diet. It offers numerous benefits, from enhancing focus and physical performance to potentially reducing the risk of certain diseases. However, it’s crucial to be mindful of your intake. Excessive caffeine can have the opposite effect, leading to health complications and diminishing its positive aspects. As with any dietary substance, the key lies in balance and understanding your body’s responses.